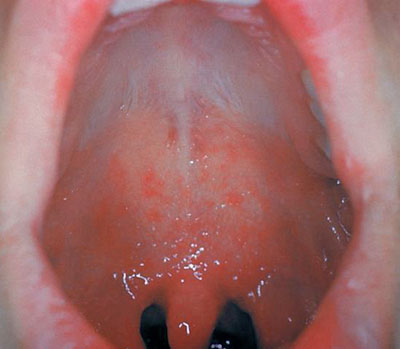
Enanthem, also known as enanthema, refers to a rash consisting of small spots that appear on the mucous membranes. This condition is often seen in patients affected by viral infections like hand, foot, and mouth disease, measles, and occasionally chickenpox or COVID-19. Moreover, bacterial infections like Scarlet fever can also cause enanthema.
Enanthema can also serve as an indicator of hypersensitivity.
Nursing Interventions
Nursing Intervention varies to the disease or medical condition:
1. Measles:
- Interventions: Isolation precautions, supportive care for symptoms like fever and discomfort, monitoring hydration and nutrition, providing clear fluids and soft foods, monitoring vital signs, administering antipyretics as needed.
2. Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease (HFMD):
- Interventions: Oral hygiene and pain management, maintaining hydration and nutrition, encouraging frequent small meals, providing cool or lukewarm liquids, avoiding acidic or spicy foods, monitoring temperature and pain level, preventing secondary infections by encouraging handwashing and avoiding close contact with others.
3. Herpes Stomatitis:
- Interventions: Topical pain relievers, maintaining oral hygiene with gentle rinses, avoiding acidic or spicy foods, managing dehydration with fluids and soft foods, providing emotional support and stress management techniques.
4. Candidiasis (Thrush):
- Interventions: Antifungal medication based on doctor's orders, maintaining oral hygiene with gentle rinses and antifungal swabs, managing discomfort with topical analgesics, ensuring adequate nutrition and hydration.
5. Allergic Reactions:
- Interventions: Identifying and avoiding the allergen, administering antihistamines as needed, monitoring for airway compromise and providing emergency care if necessary.
Common Interventions:
- Oral Care:
- Provide gentle oral hygiene with soft swabs and mouthwashes to prevent secondary infections.
- Use topical anesthetics to alleviate pain, especially during swallowing.
- Offer cool or lukewarm liquids and soft foods to avoid irritation.
- Nutrition and Hydration:
- Maintain adequate hydration through intravenous fluids if needed.
- Offer small, frequent meals of soft, bland foods to compensate for difficulty swallowing.
- Ensure proper nutritional intake to support recovery.
- Pain Management:
- Administer pain medication as prescribed by the physician to manage discomfort.
- Employ non-pharmacological pain relief methods like cool compresses and relaxation techniques.