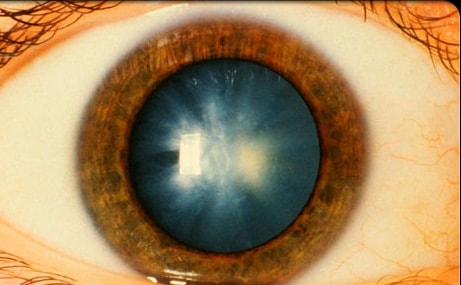
Nathalie syndrome, also known as, Deafness-cataract-skeletal anomalies-cardiomyopathy syndrome or Sensorineural hearing loss-cataract-skeletal anomalies-cardiomyopathy syndrome, is a rare, genetic developmental defect during embryogenesis disorder. The disorder is characterized by sensorineural hearing impairment, childhood-onset cataract, skeletal and cardiac anomalies, electrocardiographic abnormalities, spinal muscular atrophy, underdeveloped secondary sexual characteristics, and growth retardation. In some cases, sudden death, fatal cardiomyopathy, and heart failure may occur.
The disorder was described by a physician in 1975, in which, four siblings (three sisters and their brother) in a Dutch family had symptoms of the condition. The condition was named after the oldest sibling — Nathalie.[Source]
Nathalie syndrome can cause disability and death around early or mid adulthood. Children with this condition appear younger than their age.
Signs and Symptoms
- Sensorineural hearing impairment
- Childhood-onset cataract
- Underdeveloped secondary sexual characteristics
- Spinal muscular atrophy
- Growth retardation
- Cardiac Anomalies
- Electrocardiographic abnormalities
- Skeletal anomalies
Prevalence
< 1 / 1,000,000
Age of Onset
Childhood
Causes
Nathalie syndrome is thought to be hereditary.
Diagnosis
Various tests can help with diagnosis, including:
- Audiometry: To assess hearing.
- Ophthalmic examination: To examine the eyes for cataracts and other abnormalities.
- Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans to assess skeletal and cardiac anomalies.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To check heart rhythm.
- Electromyography (EMG): To assess muscle function.
- Genetic testing: To identify mutations associated with Nathalie syndrome.
Nursing Interventions
Sensorineural hearing impairment:
- Assess hearing ability: Regularly conduct hearing assessments to monitor changes and guide intervention choices.
- Hearing aids: Educate and assist with hearing aid selection, fitting, and usage to optimize speech and sound awareness.
- Communication strategies: Teach and encourage communication strategies like lip-reading, sign language, and assistive listening devices.
- Emotional support: Address potential social and emotional challenges arising from hearing loss and provide necessary support.
Childhood-onset cataracts:
- Monitor vision: Regularly assess visual acuity and monitor for cataract progression.
- Cataract surgery: Provide education and support before and after cataract surgery, if necessary.
- Visual aids: If vision impairment persists, assist with selecting and using appropriate visual aids like magnifiers or glasses.
- Pain management: Manage postoperative pain and discomfort efficiently.
Underdeveloped secondary sexual characteristics:
- Hormone therapy: Collaborate with specialists to manage hormone levels and promote development of secondary sexual characteristics, if indicated.
- Body image support: Address potential body image concerns and provide emotional support through this sensitive period.
- Sexuality education: Provide age-appropriate education on sexuality and sexual health considerations.
Spinal muscular atrophy:
- Positioning and mobility: Assist with maintaining proper positioning to prevent contractures and facilitate movement.
- Respiratory support: Monitor respiratory function and provide necessary support, like oxygen therapy or assisted ventilation, if needed.
- Physical therapy: Collaborate with therapists to implement personalized exercise programs to maintain muscle strength and improve mobility.
- Nutritional support: Ensure adequate nutrition intake to meet energy needs and support muscle health.
Growth retardation:
- Nutritional counseling: Consult with nutritionists to develop personalized dietary plans to promote optimal growth and development.
- Monitor growth parameters: Regularly measure height and weight to track growth patterns and identify any concerns.
- Address underlying causes: Address any underlying medical conditions contributing to growth retardation, if possible.
Cardiac and skeletal anomalies:
- Monitor vital signs: Regularly monitor heart rate, rhythm, and other vital signs to detect any abnormalities.
- Medications: Administer medications prescribed by cardiologists or other specialists to manage specific cardiac conditions.
- Orthopedic interventions: Collaborate with orthopedic specialists to provide necessary supportive devices or interventions for skeletal anomalies.
- Pain management: Address any pain associated with skeletal anomalies with appropriate pain management strategies.
Treatment
There is no cure for Nathalie syndrome, but treatment can help manage the symptoms. Treatment may include hearing aids, surgery to remove cataracts, hormone therapy, physical therapy, and other supportive measures.